
Rolled Steel is a fundamental material widely used in construction and manufacturing, known for its durability and versatility. In the words of Dr. Emily Thompson, a renowned expert in structural metallurgy, "Rolled Steel is the backbone of modern engineering, enabling the creation of robust structures that stand the test of time." This statement encapsulates the essence of rolled steel's critical role in various industries, from high-rise buildings to intricate machinery components.
The process of rolling steel involves passing it through a series of rollers to achieve desired shapes and thicknesses, significantly enhancing its mechanical properties. This method not only allows for the production of different forms such as sheets, plates, and beams but also contributes to the material's strength and flexibility. As we delve into the applications of rolled steel in construction and manufacturing, it becomes evident that its influence spans a multitude of sectors, providing essential support in creating reliable and innovative solutions.
As we explore the myriad uses of rolled steel and its significance in our daily lives, it is clear that this material is not just a commodity but a vital component of progress in engineering and design. Understanding the characteristics and applications of rolled steel will shed light on why it remains a preferred choice among engineers and manufacturers alike.
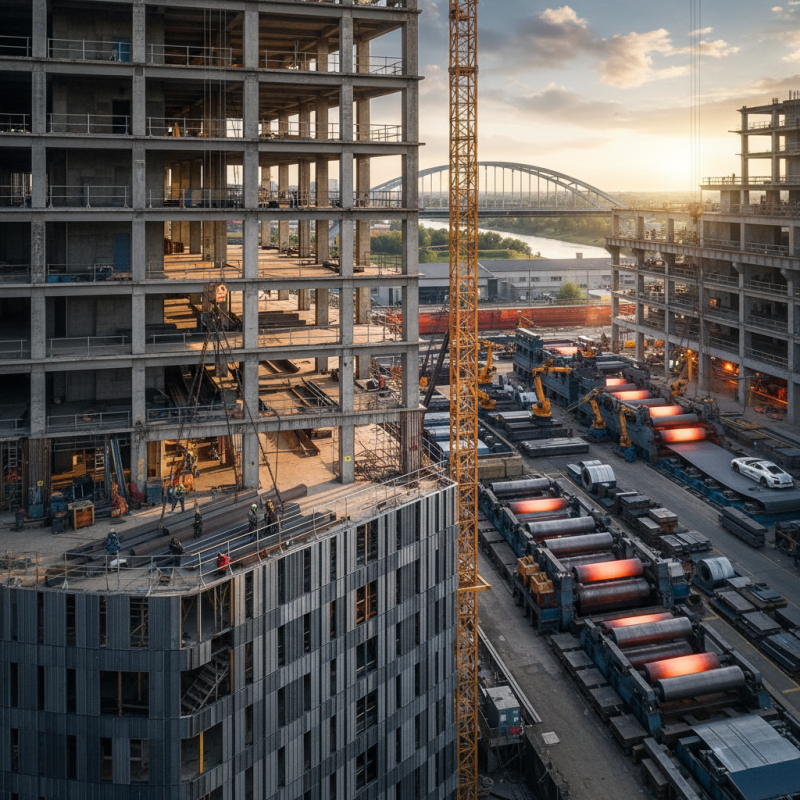

Rolled steel is a versatile form of metal created through the process of rolling, which involves reducing the thickness of steel by passing it through one or more pairs of rollers. This method allows for the creation of various shapes and sizes, making rolled steel a fundamental component in construction and manufacturing applications. The primary types of rolled steel include hot-rolled and cold-rolled steels, each possessing distinct characteristics suited for different purposes.
Hot-rolled steel is produced at high temperatures, typically above 1,700°F (927°C), which allows it to be easily shaped and formed. It generally has a rough surface finish and is used in projects where precise dimensions are not critical, such as in beams, channels, and structural components. Cold-rolled steel, on the other hand, undergoes processing at room temperature, resulting in a smoother finish with tighter tolerances, making it ideal for applications requiring precision, such as automotive parts and appliances. Understanding these types of rolled steel is essential for selecting the appropriate material for specific construction and manufacturing needs.
Rolling steel is a fundamental process in the steel industry, mainly involving the transformation of steel into various shapes and sizes through the application of compressive forces. This technique is pivotal in construction and manufacturing, as it produces steel products with enhanced strength and durability. The rolling process can be conducted hot or cold, with each method offering distinct benefits depending on the required specifications of the final product. Hot rolling occurs at elevated temperatures, making it easier to shape the steel, while cold rolling involves processing the steel at room temperature, resulting in finer surface finishes and tighter tolerances.
When rolling steel, several techniques and equipment come into play, including the use of rolling mills that consist of heavy-duty rollers to shape the metal. Modern mills employ advanced technology to control speed, temperature, and other critical parameters to ensure uniformity and quality. The configuration of rollers plays a significant role, with configurations such as two-high, three-high, and four-high setups catering to different production needs.
Tips: For those interested in the rolling process, ensure you understand the specifications required for your application. Knowing whether hot or cold rolling is appropriate can save time and money in the production phase. Additionally, familiarize yourself with the machinery used, as maintenance is key to ensuring consistent output quality and efficiency in rolling operations.
Rolled steel is a versatile material widely utilized in the construction industry due to its strength, durability, and malleability. This type of steel is produced by heating and re-shaping metal into specific forms, such as sheets, plates, or beams, which are integral in building structures. In construction, rolled steel is often used in structural applications like columns, beams, and frames, providing essential support and stability to buildings and bridges. Its resistance to adverse weather conditions also makes it a preferred choice for outdoor structures and infrastructure.
Construction professionals often prioritize rolled steel for its high strength-to-weight ratio, allowing for more efficient designs without compromising safety. Additionally, rolled steel can be easily welded or riveted, enabling seamless integration into various construction projects.
**Tips:** When selecting rolled steel for construction purposes, consider factors such as load-bearing requirements and environmental exposure. It's also beneficial to stay updated on local building codes and regulations to ensure compliance with safety standards. Utilizing quality rolled steel can significantly enhance the longevity and performance of your construction project, making it a wise investment.
Rolled steel is a fundamental material in various manufacturing industries due to its versatility and strength. Used primarily in construction, automotive, and appliance manufacturing, rolled steel comes in different profiles, including sheets, plates, bars, and beams. According to the World Steel Association, the global production of rolled steel reached approximately 1.9 billion tonnes in 2022, demonstrating its vital role in modern industry.
In construction, rolled steel is essential for structural frameworks, offering the necessary support and durability for buildings and bridges. In the automotive industry, rolled steel is utilized for body components, providing lightweight and strong materials that contribute to fuel efficiency and safety.
Tips: When selecting rolled steel for a project, it’s crucial to consider the specific requirements, such as tensile strength and corrosion resistance. Always consult the latest industry standards and seek advice from experts to ensure the chosen material meets all project demands.
Moreover, rolled steel’s application in appliances such as refrigerators and washing machines is growing, driven by the demand for energy-efficient and durable products. Manufacturers increasingly rely on rolled steel for its ability to be easily shaped and welded, enabling the production of high-quality components. Industry reports indicate that the demand for rolled steel in appliance manufacturing is anticipated to grow by 3.2% annually through 2025, reflecting its pivotal role in meeting consumer needs for reliability and sustainability.
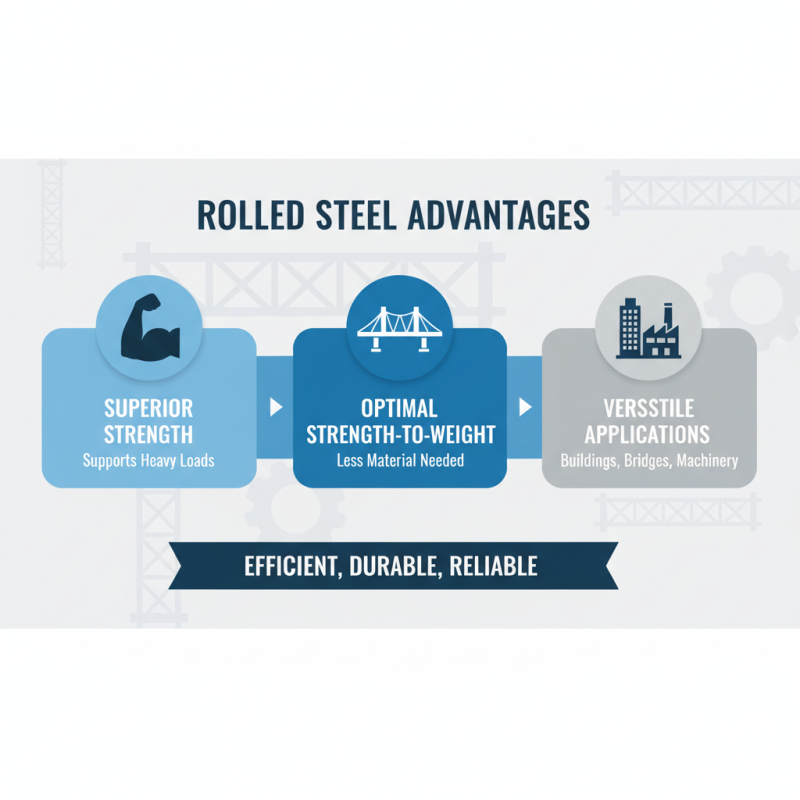
Rolled steel, a product of heating and reshaping metal into various forms, offers significant advantages over other materials in construction and manufacturing. One of the standout benefits is its strength-to-weight ratio. Rolled steel is exceptionally strong, enabling it to support heavy loads without requiring excessive material usage. This makes it an ideal choice for structural components in buildings, bridges, and industrial machinery, where maximizing strength while minimizing weight is crucial.
Another advantage of rolled steel is its versatility. It can be manufactured in various shapes and sizes, including plates, sheets, and bars, allowing for a wide range of applications in construction and manufacturing. Additionally, rolled steel is relatively easy to work with; it can be cut, welded, and formed with standard tools, which simplifies the construction process and reduces labor costs.
Tip: When selecting materials for your construction project, consider the specific strength requirements and think about how rolled steel can fulfill these needs efficiently. Additionally, always ensure that you are using the appropriate grade of rolled steel for your specific application to maximize its benefits.





